Hermaphroditic plants: definition, characteristics and examples

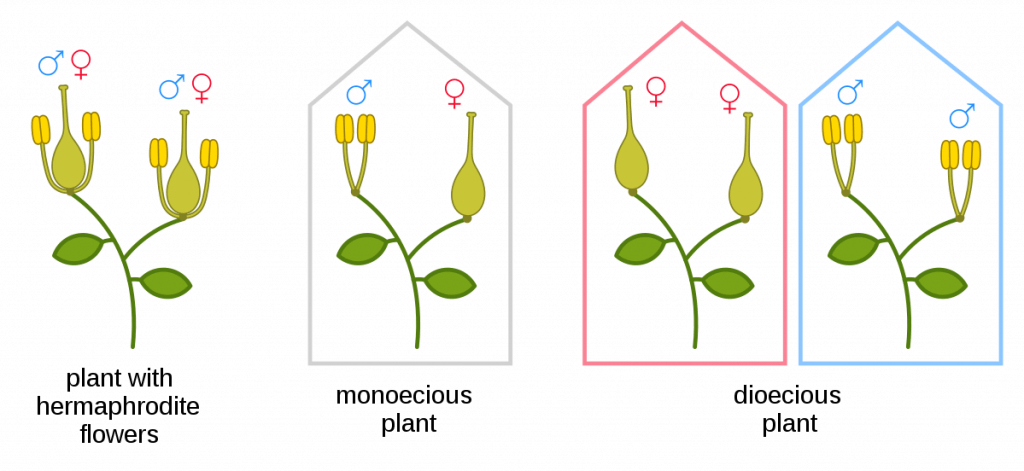
Flowering plants (angiosperms) are the most diverse group of plants on Earth, with over 300,000 species. Most plants have flowers that allow them to continue to reproduce and transmit their genes to future generations. Some species can be dioecious plants, which mean that each one is either male or female, as in humans, an individual of each sex is necessary for reproduction. They can also be hermaphroditic, which means that one plant is male and female at the same time.
Before defining hermaphroditism, we will first talk about the different constituents of the flower.
What are the parts of the male and the female flower?
The flower is a set of modified leaves, in a floral envelope and in a sexual organ, arranged on a receptacle with sepals, petals and sometimes tepals.
The male flower consists of the following parts: the floral envelope (the sterile outer petals, i.e. sepals and petals) and the stamens consisting of anthers and filaments (contain the pollen grains). In addition, the female flower consists of the floral envelope (the sterile outer petals, i.e. sepals and petals) and the carpels divided into ovary, style and stigma.
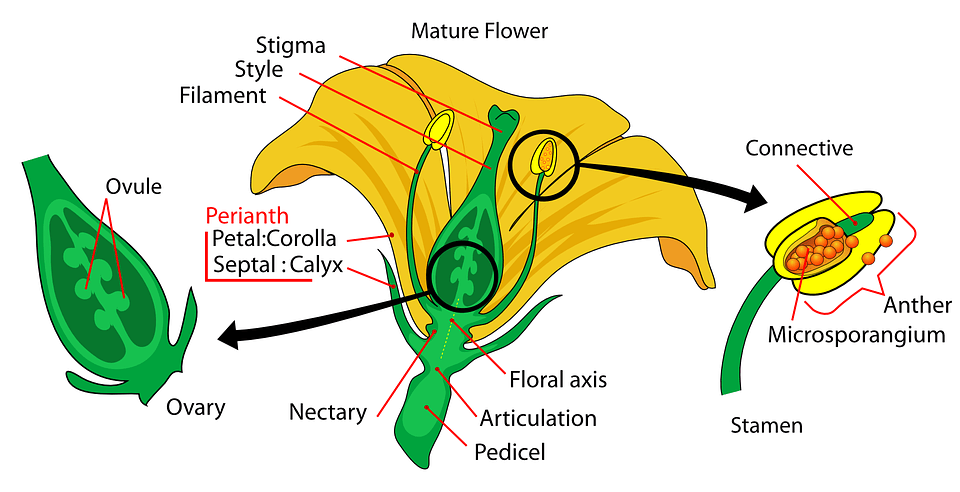
What is Hermaphrodite meaning?
Hermaphroditic plants named also bisexual plants are species that have flowers with organs of both sexes, or male flowers (with stamens) and female flowers (with pistils) on the same plant. In general, The female flowers are usually found in the lower part of the plant, while the male flowers are found at the upper end, this facilitates the transport of pollen by the wind. In fact, in the plant kingdom, the existence of hermaphrodite flowers is very common. By the way, between 75% and 90% of plants are hermaphrodites.
Characteristics
- The main characteristic of a hermaphroditic plant is that it has flowers with sexual organs of both sexes.
- Autogamy (when plants pollinate themselves) of hermaphroditic plants can improve the chances of species survival without sacrificing genetic variability.
- The advantage of many hermaphroditic plants is that they don’t rely on bees or insects in order to reproduce.
- They can reproduce easily in unfavourable environments for insects or pollinating animals.
- Some hermaphroditic plants use cleistogamy to ensure the propagation of their genetic material. Cleistogamy means that the flower does not even open its petals and sepals, but remains closed and fertilizes itself.
- Some hermaphroditic plants avoid autogamy to ensure better genetic diversity. In this case, the gametes of the different flower sexes may mature at different times so that they cannot self-fertilize, or the plant may have filters to separate its own pollen.
- Some plants can be polygamous. Polygamy differs according to the relative distribution of male and (or) female flowers on the one hand and hermaphroditic flowers on the other hand. Some plants can have hermaphroditic flowers and female flowers, others can have hermaphroditic flowers with male flowers while others can have both male and female flowers with hermaphroditic flowers.
Hermaphrodite plants examples
Two groups will be mentioned in this part. The first will include all the plants whose sexual parts, male and female, are enclosed in the same flower. The second comprises the flowers with stamens, separated from the flowers with the pistil, but on the same plant.
Plants with hermaphroditic flowers
Tomato
Tomato or Solanum lycopersicum is a plant that has hermaphroditic flowers that self-fertilize. These flowers do not produce nectar because they do not need to attract pollinators. The stamens of this plant are large and they form a closed tube that surrounds the pistil, thus guaranteeing fertilization.
Tulip

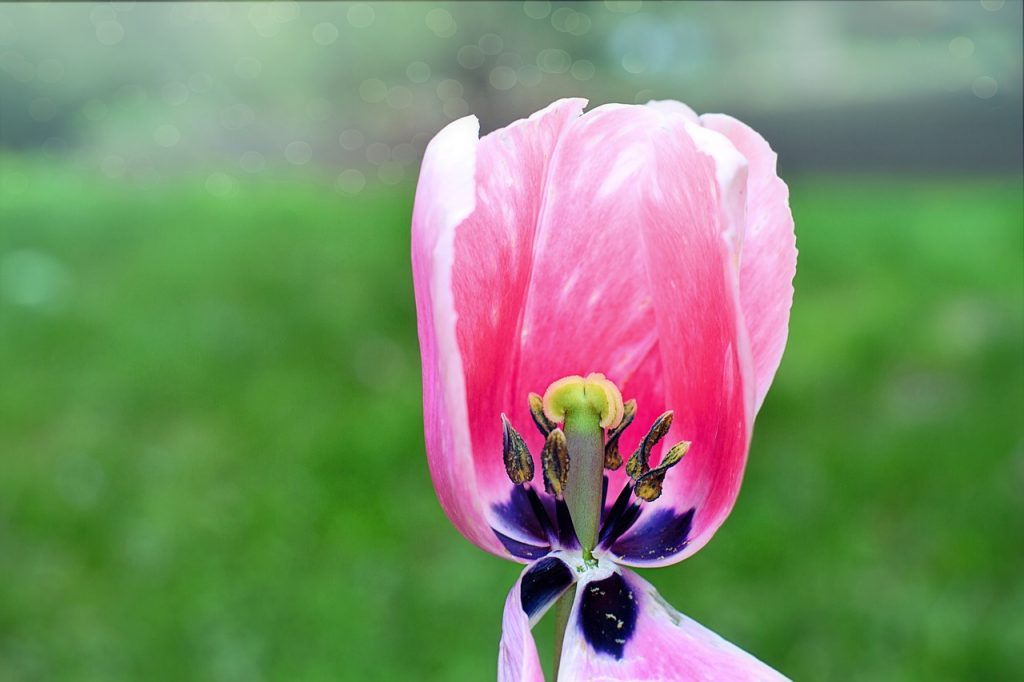
Tulip is a beautiful spring bulb flower, with many varieties. This plant belonging to the Liliaceae family have hermaphroditic flowers that bloom during spring. The flower is simple with 6 free tepals arranged in 2 whorls of 3 tepals, 6 stamens and a broad style with trilobed stigma.
Rose
The rose (Rosa) is the flower of a bushy or climbing perennial shrub from the Rosaceae family. The rosebush is characterized by its thorny stems, its generally deciduous, sometimes semi-evergreen foliage, and its roses, commonly fragrant, sometimes ascending. The rose, true queen of flower gardens, is hermaphrodite. It contains both stamens and ovary in the same flower.
Wallflower
Wallflower, or Erysimum, is a genus of flowering plants in the cabbage family, Brassicaceae. During spring and summer, these plants produce bright yellow to red or pink bilateral and hermaphrodite and ebracteate flowers.
Plants with unisexual flowers
Walnut
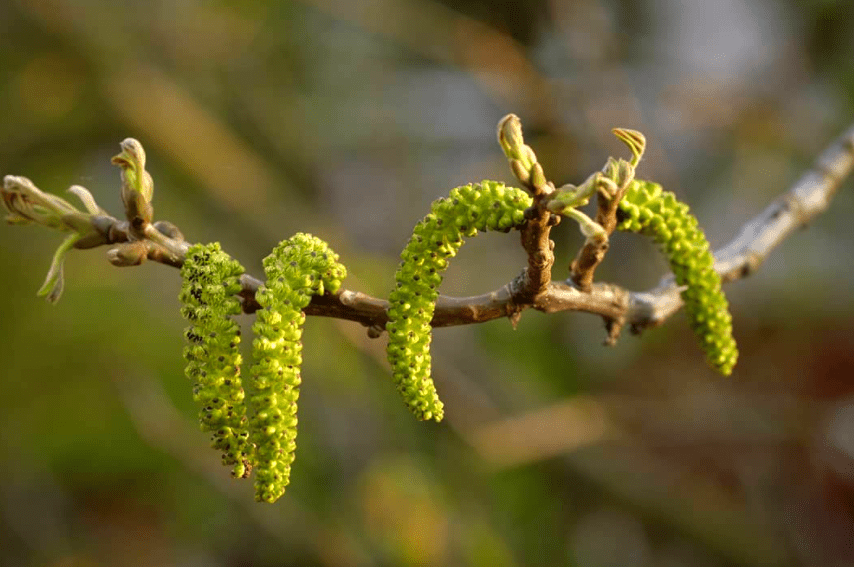

Walnut, like its closest cousins oak, hornbeam, or hazel, produces two separate types of flowers on the same tree: pollen-producing flowers (male flowers), and ovule-bearing flowers (female flowers).
The male flowers of walnut trees are the easiest to see because they are grouped in large green catkins. Each catkin consists of dozens of small flowers with numerous stamens which release pollen which fertilizes one or more female flowers.
Melon
Melon is a monoecious species that has male flowers and female flowers in different places on the same plant. At first, the male flowers appear to fertilize the female ones, which bloom 10 to 15 days after the appearance of the first flowers. Once both types of flowers are present, Pollinators pass from flower to flower, collecting pollen from the male flowers to deposit them on the pistils of the female flowers.
Squash
Squashes, Cucurbita sp, are vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family. Squashes bear both male and female flowers on the same plant. The male flowers have 5 stamens with sinuous anthers and are located under the leaves, at the end of the long stems, while the female flowers have pistil consisting of 3 carpels fused into an ovary. flowers have a short lifespan. They open in the morning and close around noon. Each female flower, therefore, has a few hours to be fertilized thanks to the intervention of bumblebees and bees.
Cucumber
This member of the Cucurbitaceae family is an annual monoecious plant that has both male and female flowers on the same plant. The small and yellow five-petalled flowers bloom in summer. A female flower can therefore be fertilized by pollen from a male flower of the same plant. However, by growing several cucumber plants (of the same variety or not), you increase the chances of obtaining many cucumbers, because cross-fertilization is more numerous than autogamous fertilization (fertilization of a plant carried out by its own pollen ).
Did you find this helpful? Share it with your friends!